Infections
Bacteria, viruses, parasites, or fungi are different types of germs which can infect the body. These germs are very small and can usually only be seen directly with special tools like microscopes. Infections can be mild or severe, depending on the type of infection and the health of the person. Many infections make people feel sick quickly after the germ gets in their body (like influenza), others can be in the body a long time before someone feels any symptoms or sickness (like HIV).
By following precautionary measures, we can keep the circle of protection strong to help prevent getting or spreading infections. Public Health has an important role in helping to protect people and communities from infectious diseases.
About infections

An infection is when germs enter someone’s body and start to make the person sick.
Precautionary measures are safety steps you can take to prevent getting or spreading infectious diseases.

If there is a large rise in the number of cases of an infectious disease, we may need to take additional precautions to keep people safe.
Explore more Infections

Avian flu (also known as H5N1) is a flu virus that mostly affects wild birds and poultry, and can lead to illness and death.
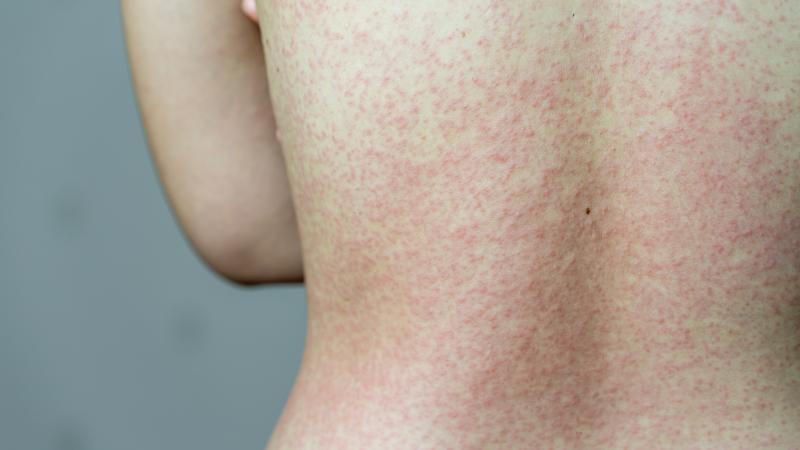
Measles is a serious and highly contagious disease caused by a virus.

Meningococcal disease is a serious infection that can cause meningitis or septicemia. It can be deadly. It’s treated with antibiotics.
The COVID-19 virus is still circulating. Follow precautions to keep the circle of protection strong around our communities.

Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is an infection caused by a virus and is common among babies and children under age 5.

Haemophilius Influenzae type a (called Hia for short) is a kind of bacteria that can cause mild to severe disease, especially in children under 5.

Influenza (flu) is a contagious lung disease caused by the influenza virus. This is a different virus than the one that causes COVID-19.

Gastroenteritis is a contagious illness that causes an upset stomach, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.

Mpox, or monkeypox, is a viral disease that can spread through close contact with someone carrying the virus.

Pneumococcal infections are caused by a bacteria called Streptococcus pneumoniae, also known as pneumococcus.

Rabies is a contagious and deadly disease.
Explore Sexually Transmitted Infections
Public Health has an important role in helping to protect people and communities from infectious diseases.
In most places, including in Eeyou Istchee, this “health protection” is a specific role for Public Health departments that is mandated under law.
Among many other functions, Public Health teams work to:
- Monitor and investigate cases of many infectious diseases so that it can be known if there is a new outbreak, or if precautions are keeping an infection under control.
- Provide support and recommendations to various community groups, community entities and to individuals to reduce the spread of those infections, and the health impacts they have on people.
- Analyze the information about infections that is collected over time, to help us better understand how an infection is transmitted, how serious it is, and whether cases are changing over time.





